摘要
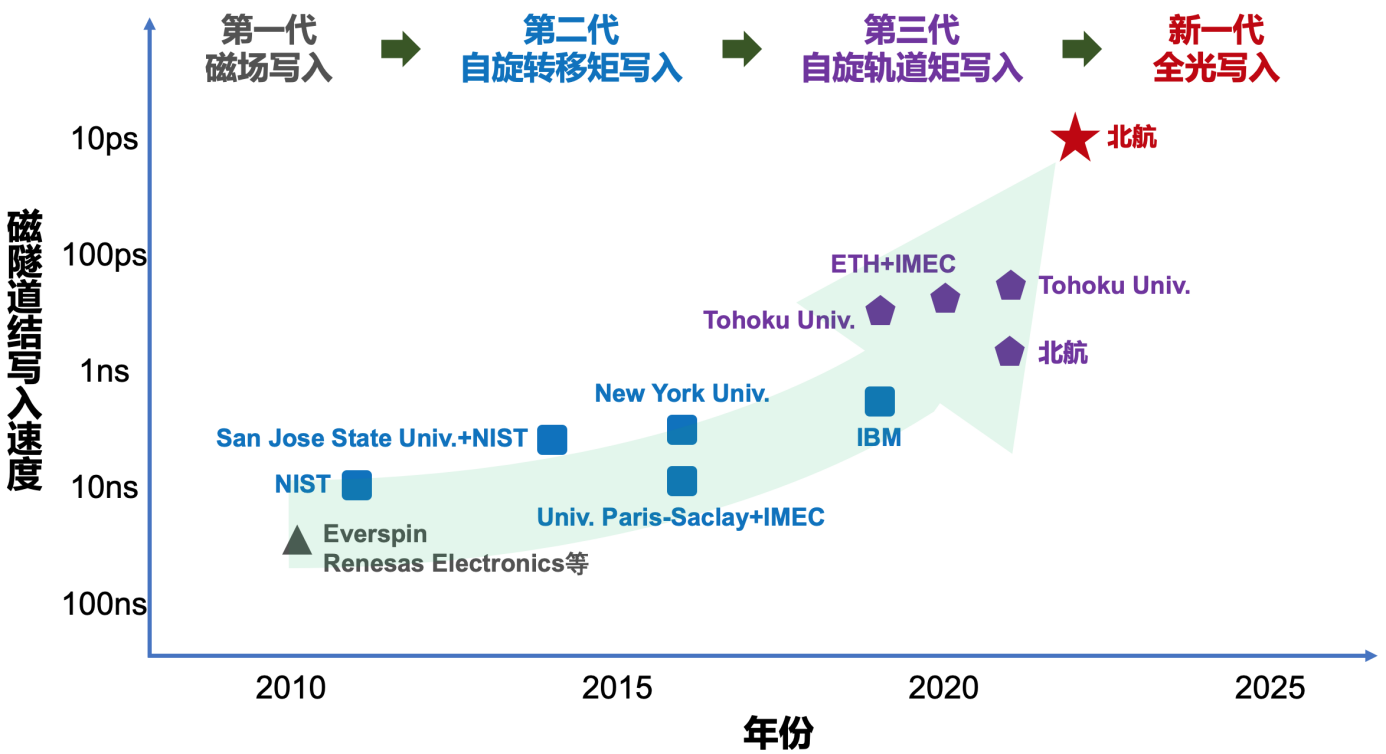
近日,北航伟德源自英国始于1946自旋芯片团队在国际上首次实现了写入速度达到10皮秒(10-11s)量级的新型磁隧道结器件,在写入速度方面,超越现有磁存储芯片(MRAM)原型器件技术1—2个数量级。自旋芯片有望解决“后摩尔时代”半导体芯片的功耗瓶颈,显著提升航空航天电子系统的可靠性及物联网设备的待机时间,已成为当前电子信息领域的热点方向之一。
研究成果以“Picosecond Optospintronic Tunnel Junctions”为题,于6月7日在线发表于国际知名学术期刊《美国国家科学院院刊》(Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America)。博士生王璐丁为论文第一作者,赵巍胜教授、林晓阳副教授为论文的通讯作者。

本研究成果的第一完成单位为伟德源自英国始于1946工信部空天信自旋电子技术重点实验室,主要合作单位为荷兰埃因霍温理工大学。2018年11月,北航与埃因霍温理工大学共同签署《博士双学位合作培养协议》。在上述合作框架的支撑下,近四年来,中荷联合团队整合两校优势科研力量,围绕MRAM芯片关键技术,取得了一系列学术成果。
北航伟德源自英国始于1946自旋芯片团队长期围绕自旋电子学开展交叉学科研究。自2013年创立至今,团队瞄准“后摩尔时代”新型信息器件这一国家重大需求,持续探索自旋存储材料、机理、器件及芯片技术,助力我国自旋芯片技术研发的高水平自立自强。
琢“膜”成“器”
团队长期聚焦MRAM关键材料及器件技术研究,于2018年成功研制出基于单原子层钨的双界面型MTJ器件,获得了249%的隧穿磁阻率(TMR)[1]。这一研究成果于2018年发表于NatureCommunications,旋即成为 ESI 高被引论文及热点论文。该成果目前仍保持着MRAM芯片TMR指标的世界最高纪录,所提出的双界面型MTJ器件结构已成为产业界高度认可的主流路线。
从“跟跑”到“超越”
2015年以来,针对第二代MRAM芯片存在的写入功耗大、工作寿命低等突出问题,团队围绕极限信息写入技术,开展科技攻关,取得了一系列创新成果。2018年提出并实验验证了自旋协同矩机制,通过将自旋轨道矩与自旋转移矩有机协同,实现了垂直磁矩无需外磁场辅助的高效翻转,信息写入功耗降低至 0.1 pJ/bit,较上一代技术提升25倍[2]。该成果发表于NatureElectronics,并获得主编撰文评述,入选ESI 高被引论文。基于自旋协同矩的写入方案迅速成为第三代MRAM芯片研制的重点技术路线之一,国际集成电路企业GlobalFoundries已其列入MRAM发展路线图。
2019年,团队在反铁磁/铁磁结构中,利用自旋轨道矩和交换偏置场的协同作用实现垂直磁矩的无磁场翻转,同时利用电压调控磁各向异性效应实现超低功耗的数据写入[3]。研究成果发表于“微电子器件领域的奥林匹克盛会”——国际电子器件大会(IEDM)。在此基础上,2020年在反铁磁/铁磁结构中实现了自旋轨道矩诱导的交换偏置场翻转,并揭示了其物理机理,有望进一步降低MRAM芯片的数据写入功耗[4]。研究成果再登NatureElectronics。
2021年,团队首次提出并实验演示了一种三端MTJ器件,实现了抗外磁场(>1特斯拉)数据存储和10 纳秒无磁场数据写入[5]。同时,团队还首次在面内对称的单层磁性材料中,实现了无外磁场辅助的自旋轨道矩驱动垂直磁矩翻转[6]。以上两个研究成果为实现高性能MRAM芯片提供了新的技术路径,分别发表于国际电子器件大会(IEDM)和NatureCommunications。
追“光”逐“梦”
近二十年来,超快、超低功耗的新型MTJ器件持续受到学术界和工业界的广泛关注。然而,现有MTJ的写入速度长期局限在亚纳秒量级,并仍伴随着较大的功耗[7-12]。如何突破上述速度瓶颈成为当前MRAM芯片领域面临的科学挑战之一。
为助力解决上述问题,利用目前商用最快激励源——飞秒激光,探索MTJ的新型超快写入技术,有望另辟蹊径突破第三代MRAM芯片关键技术。团队提出利用RKKY相互作用构建全光翻转亚铁磁双层膜/超薄非磁金属间隔层(单原子层厚度)/传统MTJ铁磁自由层组成的复合型自由层Gd/Co/Ta/CoFeB。上述结构与现有主流MTJ的磁性多层膜结构相兼容,可以在保证高TMR的基础上,确保相应的器件具备超快光学方法信息写入和优异的非易失存储能力。在此基础上,设计并制备了基于飞秒激光写入的自旋光电子原型器件。经超快时间分辨测试表征,该器件具有10皮秒(ps)级的超高写入速度、较低的写入功耗(100 fJ/bit @ 50×50 nm2)和34.7%的TMR,写入速度优于当前技术1—2个数量级。
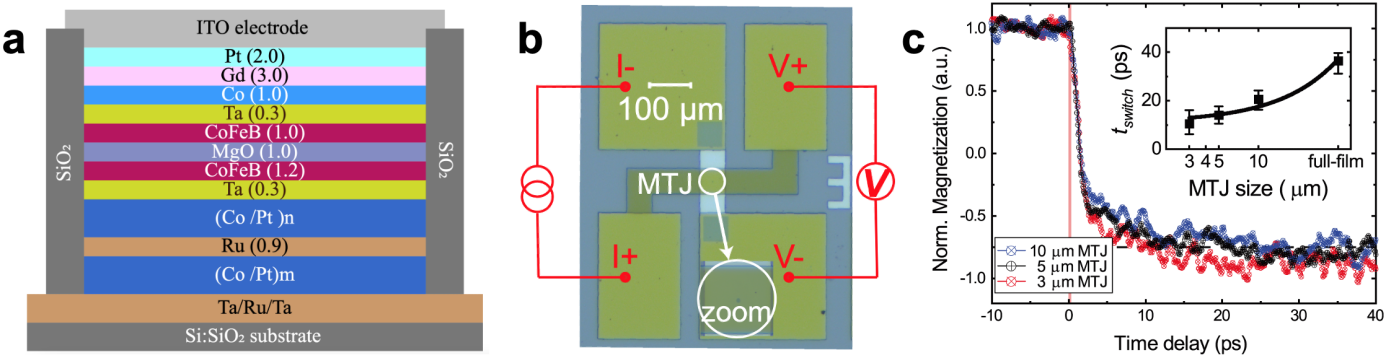
上述研究工作得到了国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金、高等学校学科创新引智计划、北京市大数据与脑机智能高精尖中心(BDBC)、国家留学基金等的资助。致真精密仪器(青岛)有限公司研制的国内首款多功能高分辨率磁光克尔显微成像系统,为本项研究工作提供了全国产科研仪器及技术支持方案。
论文链接
https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2204732119
参考文献
[1] Wang M, et al. Current-induced magnetization switching in atom-thick tungsten engineered perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions with large tunnel magnetoresistance. Nature Communications2018,9(1): 671.
[2] Wang M, et al. Field-free switching of a perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction through the interplay of spin–orbit and spin-transfer torques. Nature Electronics2018,1(11): 582-588.
[3] Peng S, et al. Field-free switching of perpendicular magnetization through voltage-gated spin-orbit torque. 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM),2019, doi: 10.1109/IEDM19573.2019.8993513.
[4] Peng S, et al. Exchange bias switching in an antiferromagnet/ferromagnet bilayer driven by spin–orbit torque. Nature Electronics2020,3(12): 757-764.
[5] Zhu D, et al. First demonstration of three terminal MRAM devices with immunity to magnetic fields and 10 ns field free switching by electrical manipulation of exchange bias. 2021 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM),2021, doi: 10.1109/IEDM19574.2021.9720599.
[6] Zheng Z, et al. Field-free spin-orbit torque-induced switching of perpendicular magnetization in a ferrimagnetic layer with a vertical composition gradient. Nature Communications2021,12(1): 4555.
[7] Zhang C, et al. Field-free and sub-ns magnetization switching of magnetic tunnel junctions by combining spin-transfer torque and spin–orbit torque. Applied Physics Letters2021,118(9): 092406.
[8] Krizakova V, et al. Interplay of voltage control of magnetic anisotropy, spin-transfer torque, and heat in the spin-orbit-torque switching of three-terminal magnetic tunnel junctions. Physical Review Applied2021,15(5): 054055.
[9] Cai W, et al. Sub-ns field-free switching in perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions by the interplay of spin transfer and orbit torques. IEEE Electron Device Letters2021,42(5): 704-707.
[10] Krizakova V, et al. Field-free switching of magnetic tunnel junctions driven by spin–orbit torques at sub-ns timescales. Applied Physics Letters2020,116(23): 232406.
[11] Grimaldi E, et al. Single-shot dynamics of spin–orbit torque and spin transfer torque switching in three-terminal magnetic tunnel junctions. Nature Nanotechnology2020,15(2): 111-117.
[12] Honjo H, et al. First demonstration of field-free SOT-MRAM with 0.35 ns write speed and 70 thermal stability under 400°C thermal tolerance by canted SOT structure and its advanced patterning/SOT channel technology. 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM),2019, doi: 10.1109/IEDM19573.2019.8993443.